Microbial identification method: molecular biology method
1, DNA base ratio
The DNA base ratio [(G+C) mol%] is expressed as the amount fraction (mol%) of the G+C substance:
(G+C) mol%=(G+C)/(A+T+G+C)%
The ratio varies widely, with prokaryotes ranging from 20-78% and eukaryotes ranging from 30% to 60%.
The convenient conclusions of DNA base composition of a large number of organisms have been determined: 1 microorganisms with close phylogenetics and highly similar phenotypes should have similar DNA base ratios; DNA base ratios between different microorganisms are very different. , which indicates that their kinship is alienated. A microorganism with the same or similar DNA base ratio does not necessarily indicate that the relationship between them is similar, because the DNA base ratio only refers to the content of four bases in the DNA, and does not reflect the base in the DNA molecule. The order in which they are arranged. 3 It is generally believed that DNA base ratios differ by more than 5% and cannot belong to the same species. DNA base ratios differ by more than 10% and may be considered as different genera.
The DNA base ratio can be determined by chemical or physical methods. At present, physical methods are commonly used for measurement, especially thermal denaturation temperature method. This method is to measure the melting temperature (Tm) of DNA using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer. Its basic principle is: first dissolve the DNA in a solution of a certain ionic strength, and then heat. When the temperature rises to a certain value, the hydrogen bond between the two nucleotide single strands is gradually opened (the DNA begins to denature) and the UV absorption of the DNA solution 365 is significantly increased; when the temperature is up to a certain value, the DNA is It is completely separated into single strands, and thereafter continues to heat up, and the UV absorption of the DNA solution is no longer increased. The thermal denaturation process of DNA (i.e., the appearance of the color enhancement effect) occurs over a narrow temperature range, and the temperature corresponding to the midpoint value of the increase in ultraviolet absorption is referred to as the thermal denaturation temperature or melting temperature of the DNA. In a DNA molecule, there are three hydrogen bonds between GC base pairs, while an AT base pair has only two hydrogen bonds. Therefore, if the bacterial DNA molecule has a high G+C content, its double-stranded binding is relatively strong, and a higher temperature is required to separate it into a single strand. In a salt solution with a certain ion concentration and a certain pH, the Tm value of DNA is directly proportional to the G+C content of DNA. Therefore, as long as the Tm value of a DNA molecule is measured by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, the G+C content of the DNA can be calculated.
2. Molecular hybridization of nucleic acids
Microorganisms with the same or similar DNA bases are not necessarily closely related. This is because the DNA base ratios are the same or similar and do not reflect the same or similar order of base pairs, and the phylogenetic relationship between microorganisms mainly depends on the order of their base pairs. Therefore, to determine the affinities between them, molecular hybridization experiments of nucleic acids are performed to compare the degree of base pair sequence between them. The application of molecular hybridization test of nucleic acid in microbial classification and identification mainly includes methods such as DNA-DNA molecular hybridization and DNA-rRNA molecular hybridization.
1DNA-DNA hybridization: The basic principle of this method is to use DNA double strands to dissociate into single strands (denaturation), single strands to form double strands (refolding), base pairing specificity, and DNA from different sources Melt in vitro and, under suitable conditions, allow complementary base pairing in a single strand to bind to double stranded DNA. The percentage of heterozygosity is then determined based on the ability to generate double strands.
The specific determination method of molecular hybridization of nucleic acid can be divided into liquid phase hybridization and solid phase hybridization according to the environment of the hybridization reaction, the former is carried out in a solution, and the latter is carried out on a solid support. Among these methods, some require isotopically labeled DNA, and some are labeled with non-isotopes. In the classification of bacteria, solid phase hybridization is commonly used for measurement. The general approach of this method is to pre-fix the single-stranded DNA of each unlabeled microbial strain on a nitrocellulose microporous membrane (or agar, etc.), and then use the single-stranded DNA small molecule of the isotopically labeled reference strain. The fragment hybridizes to the single strand of DNA on the membrane under the conditions of Zui's suitable temperature; after the hybridization is completed, the unpaired labeled labeled DNA fragment on the filter is washed away; and then the radioactivity of the DNA filter of each strain is determined. The relative percentage of hybridization of other strains to the reference strain can be calculated by taking the radioactive count value of the reference strain's self-refolding binding to 100%. These percentage values ​​represent the level of homology or similarity between these strains and the reference strain, respectively, and the value of each species is judged by this value.
2DNA-rRNA Molecular Hybridization: DNA (G+C) mol% determination and DNA-DNA molecular hybridization methods open up new avenues for the classification and identification of microbial species and genera, and solve the problem that cannot be solved based on phenotypic characteristics. Some difficult questions. Many studies have shown that when the DNA pairing bases of the two strains are less than 20%, DNA-DNA hybridization often cannot form double strands, thus limiting the application of DNA-DNA molecular hybridization methods in the classification of microorganisms. When the DNA-DNA hybridization rate of the two strains is low or cannot be hybridized, DNA-rRNA hybridization may still have a higher hybridization rate, and thus can be used to further compare the relationship between the more distant strains, and to perform the genus. It belongs to the classification of the above classification units. The principles and methods of DNA-rRNA hybridization and DNA-DNA hybridization are basically the same, and all utilize the law of nucleic acid renaturation. But there are differences between the two methods:
A. In the hybridization of DNA-rRNA molecules, the isotope-labeled site is in rRNA.
B. DNA-rRNA molecular hybridization results are expressed as Tm values. The higher the Tm value, the closer the kinship is.
3 Nucleotide sequence analysis As can be seen from the chapter * section, 16SRNA macromolecules play an important role in the study of biological evolution. Compared with the traditional bacterial classification system, the new bacterial classification system also has many differences, which are mainly manifested in:
A. Changed the cell wall structure as one of the markers of kinship division, such as mycoplasma without cell wall, which is actually a progeny branch of Gram-positive Clostridium sp.
B. Changed the type of nutrition as a phylogenetic feature. For example, photosynthetic bacteria are not independent of the evolutionary branches of non-photosynthetic populations, but each photosynthetic population represents a higher-order taxa, and its progeny branches include non-photosynthetic bacteria. .
C. Although Gram-positive bacteria are a group of bacteria closely related to phylogeny, Gram-negative bacteria include 10 sub-populations.
Finished Products of varicella vaccine. It has three qualities,good safety of gelatin-free, long validity period by good stability, better protection with high titer and immune efficacy. These improvements enhanced the vaccine safety and quality, and established BCHT the leading position in varicella vaccine. We have two different packages, penicillin bottle and pre-filled syringe. And it has been exported to other countries, such as India, Philippines.
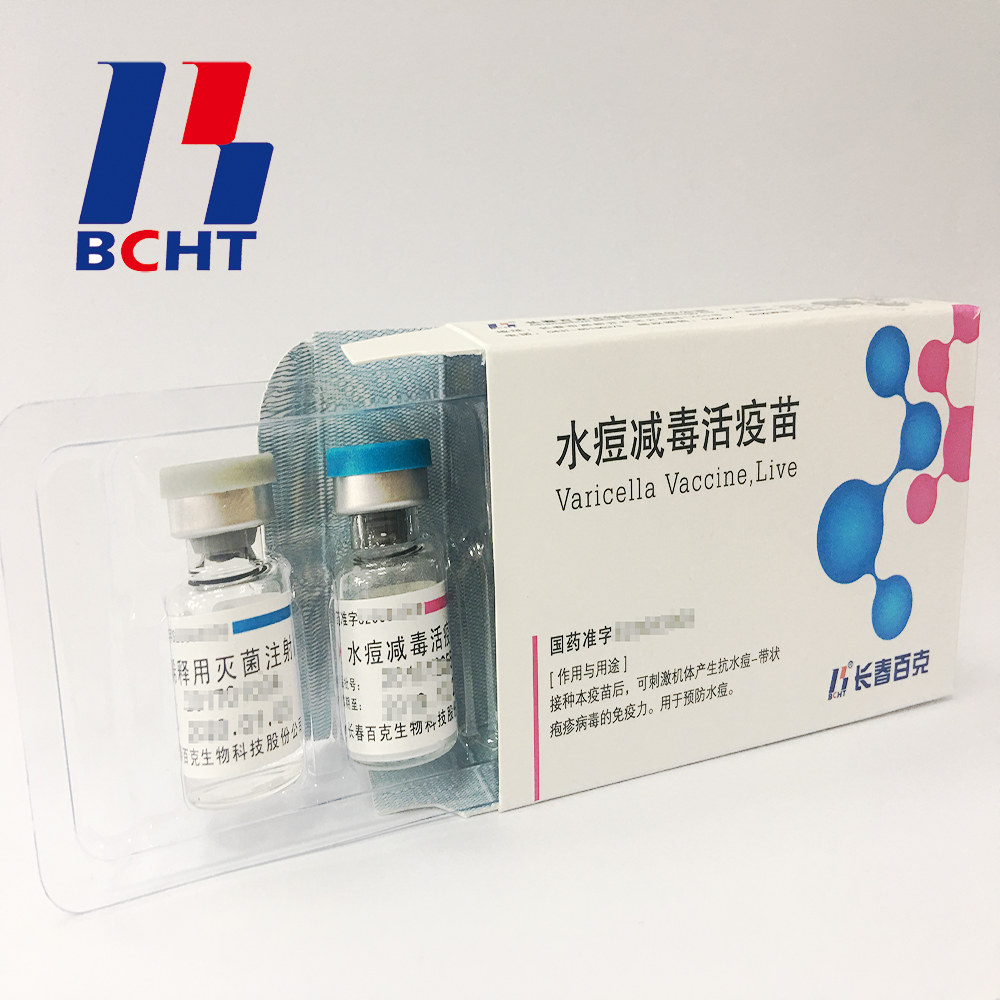
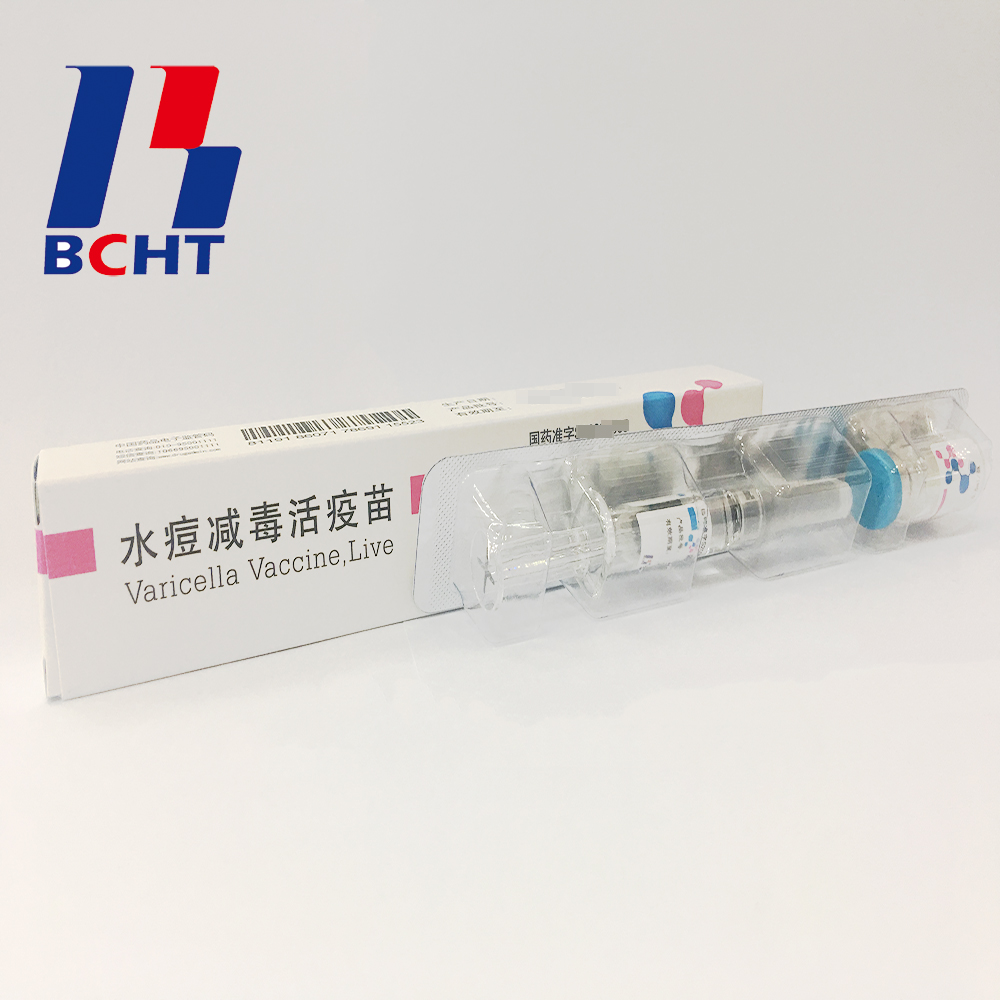
Finished Products
Finished Products Of Rabies Vaccine,Rabies Vaccine For Human Use,Live Biotechnology Chicken Pox,Live Lyophilized Vaccination
Changchun BCHT Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.ccbcht.net