Problems and countermeasures of raising newborn lambs
Lack of colostrum
As soon as possible, the countermeasures allow the lamb to eat colostrum. The amount of colostrum taken by the lamb is roughly 5% of its live weight. For example: 1 lamb of 4.5 kg should eat 225 grams of colostrum, of which, after birth, the sooner you eat, the better the other half is. Eat within 10-12 hours thereafter.
Ewes lack milk
After the lamb is born, she does not have access to mother's milk and her body becomes weaker, often dying due to hunger.
A necropsy of dead lambs, no contents in the stomach and no fat spots. In normal lambs, there should be a small amount of fat around the heart, small intestine, and kidneys.
Countermeasure 1 Find out as soon as possible, artificially warming, and diligently measure body temperature. 2 Feed 1/3-1/2 cups of colostrum in time to enhance lamb's resistance. When the lamb is larger, use manual feeding to feed the bottle at 1/5 of live weight and feed it with a bottle, 2 times sooner or later. 3 Inject 50 ml of 10% glucose solution subcutaneously. 4 Carefully check the ewe and eliminate the cause. 5 Strengthen prevention. Measure the body temperature of lambs in wet and cold weather. Check whether the lamb is full or not. When feeding, separate lambs often steal milk from the ewes. In general, the head of such lambs has yellow stains that are easily discernible. They should promptly take measures to strengthen breastfeeding or feed in advance.
Umbilical cord infection
The newborn lamb's umbilical cord is a hollow tube with a thickness of 0.6-1.2 cm. It is directly connected to the abdominal cavity and connected to the liver. It can not dry out after a few days after birth, and it is the passage for bacteria to invade the sheep in vitro. There is also a umbilical cord infection. The lamb does not show symptoms until 3 weeks of age. However, there are abscesses, fevers, and difficulty walking in the joints. If they do not keep up with the ewes, they are less likely to be suckled and eventually die of hunger.
Countermeasures Lambs are immersed in umbilical cords with iodine when they are born.
diarrhea
Lambs are prone to water diarrhoea when they have not been transferred out of their lambs within 3 days of age. After 5-7 days of age, the small intestine function of the lamb began to be perfect, which can alleviate the effect of digestion of bacteria, resulting in less morbidity.
Because of the young lambs, only 1-3 days old, they cannot stand up to bacterial infections, and they mainly do prevention work. 1 The ewes were injected with E. coli vaccine preparation 30 days before delivery. However, it should be noted that the short period of validity may have little effect on lambs born in the late lambing period. 2 The ewes sheared hair 30-45 days before lambing or cut the hairs of the breasts. All ewes cannot step on mud and dirt slurry.
3 It is forbidden to repeat the use of pre-swept mat grass, nor can it be used for laying maternal sheep homes.
Type C enterotoxemia
This is a disease caused by a clostridial spore toxin that is present in the soil. Mainly seen in the nutritional disorders of 1-2 weeks old lambs, such as eating too much food, starting feeding or a sudden increase in the amount of milk (commonly found in the death of a lamb when the twin lamb). After the lamb is infected, it has a fast onset, often suddenly dies, or has abdominal pain, convulsions, and dies within 2-12 hours. Sometimes bloody sputum was found. The dead lambs were examined and there were hemorrhagic black spots in the small intestine.
The countermeasures are too fast and difficult to treat. They mainly do preventive work. 1 Ewes were injected 30 days before delivery. 2 Lambs born to unvaccinated ewes were given a vaccine at 2 to 3 days of age and 1 injection at 2 weeks of age. 3 Inject 5-10 ml of antiserum subcutaneously.
A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)(PICC Line) is widely used in transfusion therapy and for monitoring many kinds of diseases, especially in critically ill patients. Compared with other catheters, it has a lower risk of catheter-related bloodstream infections.
Intravenous or IV therapy is beneficial for several conditions and medical situations including dehydration, nutrition, shock, surgery, blood transfusions, chemotherapy and medication administration.
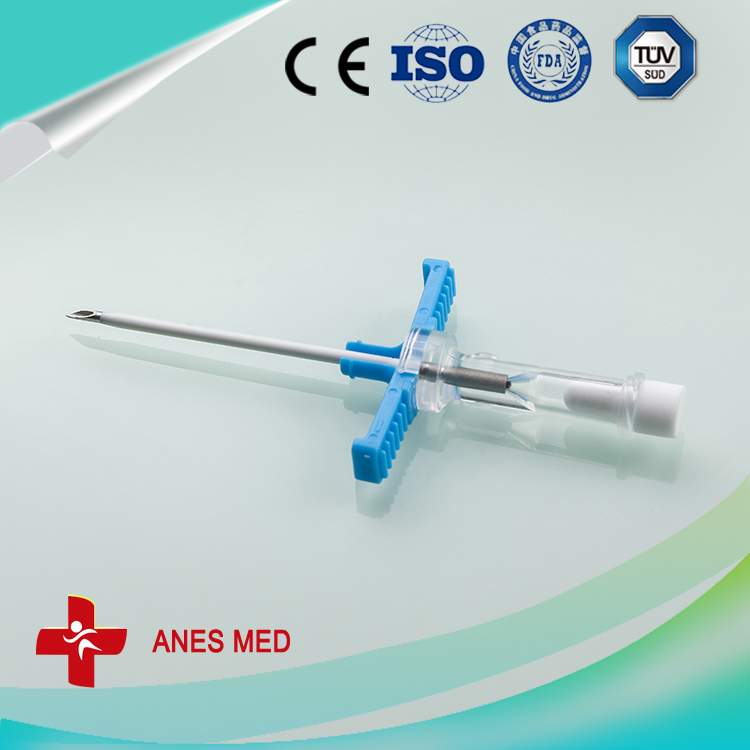
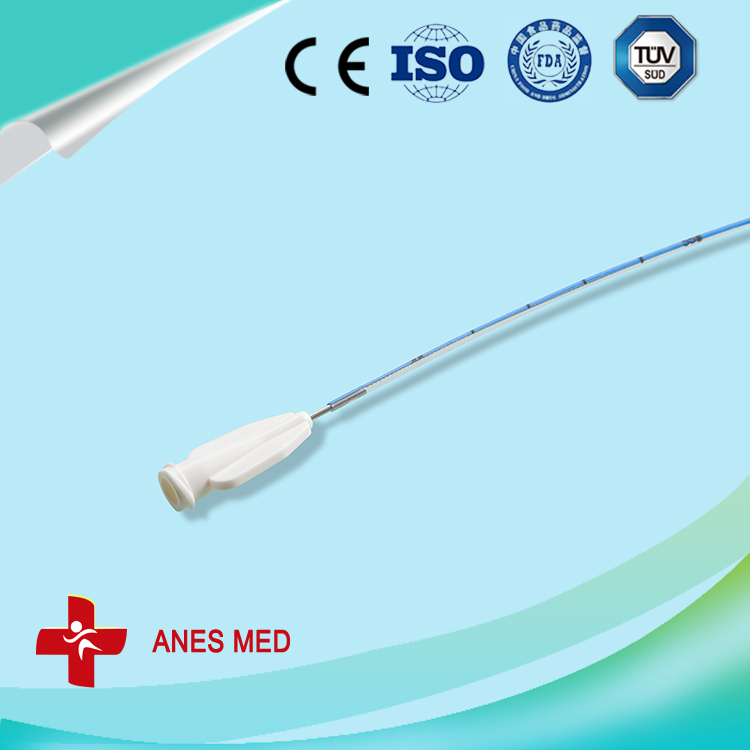
Peripheral Inserted Central Catheter(picc)
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter,Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter Kit,Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter Line Kit,PICC Line
Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , http://www.sinoanesthesia.com