Nectarine tree fertilization technology
First, peach tree needs fertilizer characteristics
(A) Peach's requirements for the environment Peach has a wide range of temperature adaptation and can be cultivated at an average annual temperature of 8-17°C. The most suitable growth temperature is 18-23°C. It is about 25 degreeC. If the temperature is too low, it may cause freezing damage and poor tree growth. If it is too high, it can easily cause burns to the branches. Peach in the dormant period needs a period of low temperature to make the peach bud normal development, otherwise it is easy to cause the germination is not neat and there are buds dead.
Peach is a fruit tree with high lightness. Pay attention to the sunny plot when choosing a garden.
Peach trees like to dry, poor tolerance to waterlogging, too much rain or long time, the higher soil moisture content can cause the branches to be slightly longer, the flower buds are not easy to form, the fruit yield is reduced, and the taste is worse.
Peach trees have a strong ability to adapt to the soil. Generally, the soil can be planted, and the soil with neutral acidity grows well. Soil pH below 4 or above 8 severely affects growth. For the adaptation of soil texture, it is well cultivated in sandy loam with good drainage, strong permeability, and fertile soil. It shows early results and good quality; if the soil is too fertile and the texture is too thick, it is easy to grow too prosperous. The results were later, the early yield was low, the quality was poor, and the taste was light and the fruit was small.
(b) the nutritional characteristics of peach trees peach tree is the most hi light, the results of early, weak fast, short life. Generally 2-3 years results, 5-15 years full fruit period.
1. Peach trees have the characteristic of storing nutrients. The flower bud differentiation and flowering results of peach trees are completed within two years. The tree of peach tree has the characteristics of storage and nutrition. The level of nutrition in the previous year not only affected fruit production in the year, but also had a direct impact on the flowering results in the coming year. Studies have shown that in the early weeks of the peach tree germination, the main use is the storage of nutrients in the tree. Therefore, the amount of nutrients accumulated and accumulated in peach trees in the fall of the previous year had a great influence on flower bud differentiation and flowering in the second year, which in turn affected peach tree yield. In terms of the regulation of fertilizer in peach trees, it is necessary to have a global perspective. After the harvest of peaches, fertilizer and water management must still be strengthened.
2. Root characteristics of peach trees The roots of peach trees are shallow, and the absorption roots are mainly distributed in 10-30 cm; however, the root system is more developed, with more lateral roots and fibrous roots, and the ability to absorb nutrients is stronger. In order to prevent the root system from going up too much and affecting the tree's solidity and drought resistance in production, it is necessary to pay attention to proper deepening or combination of deep application and shallow application in the fertilization of peach trees.
Peach's root system requires better soil aeration conditions, and the soil's ventilation pore volume is better at 10%-15%. To ensure that the root system has better respiratory conditions, pay attention to the application of organic fertilizer in the fertilization, and moderately mix the organic fertilizer with the soil to increase the granule structure of the soil and increase the air content of the soil. Where conditions permit, green manure can be planted under the peach tree to turn over and increase the organic matter content of the soil to improve the ability of the soil to regulate water vapor.
3. Peach's nutritional characteristics Peach saplings are more prosperous and have greater absorptive capacity. The demand for nitrogen is not too high. If more nitrogen is used, it can easily lead to excessive vegetative growth and flower bud differentiation is difficult. Entering the end of the result, it is easy to cause physiological fruit drop. After the result has reached the peak, the absorption capacity of the root system has been reduced, and the demand for nutrients from the tree has become more. If the supply of nitrogen is insufficient, the tree vigor is easily weakened, the resistance is poor, the yield is low, and the life span is shortened. Therefore, in the nutritional requirements of peach trees, the young trees are dominated by phosphate fertilizers, with appropriate amounts of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers, and mainly long-rooted trees. After entering the full fruit period, the focus of fertilization is to coordinate the growth of the branches and the flowering of peach trees. Nitrogen and potassium fertilizers are mainly used in fertilization, and a certain amount of phosphate fertilizer and trace elements are applied.
4. The effects of rootstocks on nutrient absorption and utilization The use of different rootstocks also has a significant impact on the growth and nutrient uptake of peach trees. For example, with rootstocks such as nectarine, the grafted cultivars are characterized by well-developed root systems, strong nutrient absorption capacity, tolerance to infertility and drought, and long life span; however, the soil is very fertile and prone to overgrowth. Such as poor drainage or low-lying wetlands, easy to grow poorly, eventually results in poor peach trees. Podocarpus was used as the rootstock, which was characterized by large and deep roots, less fine roots, less ability to absorb nutrients, better early fruitability, and stronger cold and salt tolerance. The disadvantage was poor results in warm areas.
Second, peach tree fertilization technology
(a) Peach's need for nutrients The test data from various regions indicate that the peach tree needs to absorb 0.3-0.6 kg of nitrogen for every 100 kg of peach fruit, 0.1-0.2 kg of absorbed phosphorus, and 0.3 kg of absorbed potassium. -0.7 kg. Due to factors such as nutrient loss, soil fixation, and different absorption capacity of the root system, the application amount of fertilizer varies greatly due to the differences in soil types, peach varieties, and the level of management. The annual nitrogen fertilizer application in high yield Taoyuan The amount of pure nitrogen is 20-45 kg, the application amount of phosphorus fertilizer is 4.5-22.5 kg as phosphorus pentoxide, and the application amount of potassium fertilizer is 15-40 kg as potassium oxide. Peach also needs trace elements and nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, which are mainly supplied by soil and organic fertilizers. Peaches with less soil and less organic fertilizer can be trace mineral fertilizers.
(B) Application of fertilizers The application amount of fertilizers in peach trees should be determined flexibly based on the soil fertility, age, species, yield, and climate factors. In the orchards with low soil fertility, high tree age, and high yield, the amount of fertilization is higher; the fertilization of orchards with high soil fertility, low age, and low yield is appropriately reduced. The varieties are more resistant to fertilizers, suitable for climatic conditions, and have a higher amount of water for moderate fertilizers. On the contrary, the amount of fertilizers should be appropriately reduced. If the application amount of organic fertilizer is more, the application amount of chemical fertilizer should be less.
Peach's fertilization period is: base fertilizer, promote flower fertilization, sit fruit fertilizer, fruit enlargement fertilizer.
1. The application of basal fertilizer is based on the difference in different varieties of peach trees. The fertilization time should be applied as soon as possible after the fruit is picked. If the fertilizer cannot be applied in time, it can be applied about one month before the peach defoliation.
2. In the application of basal fertilizers, organic fertilizers are preferred. Under the condition of less organic fertilizer, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer can be determined flexibly according to the age of trees, the growth of peach trees, and the fertility of the soil. The application rate of nitrogen fertilizer in general basal fertilizer accounts for about 40%-60% of the total annual amount of fertilizer. The amount of fertilizer applied per adult peach tree is equivalent to 0.3-0.6 kg of pure nitrogen (equivalent to 1.7-3.4 kg of ammonium bicarbonate or urea 0.6- 1.3 kg or ammonium nitrate 0.9-1.9 kg). General phosphate fertilizer is mainly used as basal fertilizer. If more organic fertilizer is applied at the same time, the pure phosphorus pentoxide equivalent per plant is 0.3-0.5 kg (corresponds to 25% of superphosphate with a phosphorus content of 2-3.3 kg or phosphorus 40% ammonium phosphate 0.75-1.25 kg). The amount of potash used in general basal fertilizers is equivalent to 0.25-0.5 kg of pure potassium oxide (corresponding to 0.5-1 kg of potassium sulfate containing 50% of potassium oxide or 0.4-0.8 kg of potassium chloride containing 60% of potassium oxide). Pay attention not to rely too close to the tree body during fertilization. Fertilizer should be properly mixed with the soil to avoid burning roots. Peach trees with more soil moisture content, soil texture more viscous, older tree age, and weaker tree vigor may use higher amounts of fertilization when applying less organic fertilizer, and vice versa.
3. The application of flower-enhancing fertilizers promotes application of flowering fertilizers before flowering in early spring. Fertilizers are mainly nitrogenous fertilizers, accounting for about 10% of the annual fertilization amount, and are combined with irrigation water after the spring, and the nitrogen fertilizer consumption per 667 m 2 is pure nitrogen. It is calculated as 2-5 kilograms (approximately 4.3-10.9 kilograms of urea or 11-28.6 kilograms of ammonium bicarbonate). If the application rate of basal fertilizer is arrogant or the basal fertilizer applied in winter, the application of flower-fertilizer may not be applied or reduced.
4. The fruit-bearing manure application was mostly applied after flowering and before fruit nucleation, mainly to increase fruit setting rate, improve tree nutrients, and promote rapid fruit growth in the early stage. Nitrogen fertilizer is the main fertilizer, with a small amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. The dosage is about 10% of the annual application amount, and the amount of nitrogen fertilizer per acre is 2-5 kilograms in terms of pure nitrogen (approximately 4.3-10.9 kilograms of urea or 11-28.6 kilograms of ammonium bicarbonate).
5. Application of fruit enlargement fertilizer The fruit enlargement fertilizer is applied after the fruit enters the rapid growth period again. The fruit enlargement period of mid-late maturing varieties basically coincides with the flower bud differentiation period. At this time, top dressing promotes rapid fruit growth and promotes flower bud differentiation, which will be used for the next year's production. A good foundation is of great significance. The fruit enlargement fertilizer is dominated by nitrogen and potassium fertilizers, and a certain amount of phosphate fertilizer can be appropriately applied according to the phosphorus supply status of the soil. The amount of fertilizer used accounts for about 20%-30% of the annual application amount, and the amount of nitrogen fertilizer per 667 m 2 is 4-10 kg in terms of pure nitrogen (approximately 8.6-20.8 kg of urea or 22-57.5 kg of ammonium bicarbonate); potassium fertilizer For every 667m2 application, 6-15kg in terms of potassium oxide (approximately 12-30kg of potassium sulfate containing 50% of potassium oxide or 10-25kg of potassium chloride containing 60% of potassium oxide). . If necessary, 10-30 kg of superphosphate containing 14%-16% of phosphorus pentoxide can be formulated.
6. Peach has less demand for trace element fertilizers, mainly relying on organic fertilizers and soils. If organic fertilizers are used more, they may not be applied or applied less; trace organic fertilizers may be applied less if organic fertilizers are used less frequently. The actual amount of trace fertilizer is calculated as base fertilizer for specific fertilizers: borax 667 m2 dosage 0.25-0.5 kg, zinc sulfate 667 m2 dosage 2-4 kg, manganese sulfate 667 m2 dosage 1-2 kg, ferrous sulfate 667 m2 dosage 5-10 kg (should be used together with high-quality organic fertilizer, the ratio of the ratio of organic fertilizer and iron fertilizer 5:1), micro-fertilizer can also be foliar spray, the concentration of spraying according to the degree of aging leaves The control is 0.1%-0.5%. It should be thin when the leaves are tender and thick when the leaves are older.
(A) Peach's requirements for the environment Peach has a wide range of temperature adaptation and can be cultivated at an average annual temperature of 8-17°C. The most suitable growth temperature is 18-23°C. It is about 25 degreeC. If the temperature is too low, it may cause freezing damage and poor tree growth. If it is too high, it can easily cause burns to the branches. Peach in the dormant period needs a period of low temperature to make the peach bud normal development, otherwise it is easy to cause the germination is not neat and there are buds dead.
Peach is a fruit tree with high lightness. Pay attention to the sunny plot when choosing a garden.
Peach trees like to dry, poor tolerance to waterlogging, too much rain or long time, the higher soil moisture content can cause the branches to be slightly longer, the flower buds are not easy to form, the fruit yield is reduced, and the taste is worse.
Peach trees have a strong ability to adapt to the soil. Generally, the soil can be planted, and the soil with neutral acidity grows well. Soil pH below 4 or above 8 severely affects growth. For the adaptation of soil texture, it is well cultivated in sandy loam with good drainage, strong permeability, and fertile soil. It shows early results and good quality; if the soil is too fertile and the texture is too thick, it is easy to grow too prosperous. The results were later, the early yield was low, the quality was poor, and the taste was light and the fruit was small.
(b) the nutritional characteristics of peach trees peach tree is the most hi light, the results of early, weak fast, short life. Generally 2-3 years results, 5-15 years full fruit period.
1. Peach trees have the characteristic of storing nutrients. The flower bud differentiation and flowering results of peach trees are completed within two years. The tree of peach tree has the characteristics of storage and nutrition. The level of nutrition in the previous year not only affected fruit production in the year, but also had a direct impact on the flowering results in the coming year. Studies have shown that in the early weeks of the peach tree germination, the main use is the storage of nutrients in the tree. Therefore, the amount of nutrients accumulated and accumulated in peach trees in the fall of the previous year had a great influence on flower bud differentiation and flowering in the second year, which in turn affected peach tree yield. In terms of the regulation of fertilizer in peach trees, it is necessary to have a global perspective. After the harvest of peaches, fertilizer and water management must still be strengthened.
2. Root characteristics of peach trees The roots of peach trees are shallow, and the absorption roots are mainly distributed in 10-30 cm; however, the root system is more developed, with more lateral roots and fibrous roots, and the ability to absorb nutrients is stronger. In order to prevent the root system from going up too much and affecting the tree's solidity and drought resistance in production, it is necessary to pay attention to proper deepening or combination of deep application and shallow application in the fertilization of peach trees.
Peach's root system requires better soil aeration conditions, and the soil's ventilation pore volume is better at 10%-15%. To ensure that the root system has better respiratory conditions, pay attention to the application of organic fertilizer in the fertilization, and moderately mix the organic fertilizer with the soil to increase the granule structure of the soil and increase the air content of the soil. Where conditions permit, green manure can be planted under the peach tree to turn over and increase the organic matter content of the soil to improve the ability of the soil to regulate water vapor.
3. Peach's nutritional characteristics Peach saplings are more prosperous and have greater absorptive capacity. The demand for nitrogen is not too high. If more nitrogen is used, it can easily lead to excessive vegetative growth and flower bud differentiation is difficult. Entering the end of the result, it is easy to cause physiological fruit drop. After the result has reached the peak, the absorption capacity of the root system has been reduced, and the demand for nutrients from the tree has become more. If the supply of nitrogen is insufficient, the tree vigor is easily weakened, the resistance is poor, the yield is low, and the life span is shortened. Therefore, in the nutritional requirements of peach trees, the young trees are dominated by phosphate fertilizers, with appropriate amounts of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers, and mainly long-rooted trees. After entering the full fruit period, the focus of fertilization is to coordinate the growth of the branches and the flowering of peach trees. Nitrogen and potassium fertilizers are mainly used in fertilization, and a certain amount of phosphate fertilizer and trace elements are applied.
4. The effects of rootstocks on nutrient absorption and utilization The use of different rootstocks also has a significant impact on the growth and nutrient uptake of peach trees. For example, with rootstocks such as nectarine, the grafted cultivars are characterized by well-developed root systems, strong nutrient absorption capacity, tolerance to infertility and drought, and long life span; however, the soil is very fertile and prone to overgrowth. Such as poor drainage or low-lying wetlands, easy to grow poorly, eventually results in poor peach trees. Podocarpus was used as the rootstock, which was characterized by large and deep roots, less fine roots, less ability to absorb nutrients, better early fruitability, and stronger cold and salt tolerance. The disadvantage was poor results in warm areas.
Second, peach tree fertilization technology
(a) Peach's need for nutrients The test data from various regions indicate that the peach tree needs to absorb 0.3-0.6 kg of nitrogen for every 100 kg of peach fruit, 0.1-0.2 kg of absorbed phosphorus, and 0.3 kg of absorbed potassium. -0.7 kg. Due to factors such as nutrient loss, soil fixation, and different absorption capacity of the root system, the application amount of fertilizer varies greatly due to the differences in soil types, peach varieties, and the level of management. The annual nitrogen fertilizer application in high yield Taoyuan The amount of pure nitrogen is 20-45 kg, the application amount of phosphorus fertilizer is 4.5-22.5 kg as phosphorus pentoxide, and the application amount of potassium fertilizer is 15-40 kg as potassium oxide. Peach also needs trace elements and nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, which are mainly supplied by soil and organic fertilizers. Peaches with less soil and less organic fertilizer can be trace mineral fertilizers.
(B) Application of fertilizers The application amount of fertilizers in peach trees should be determined flexibly based on the soil fertility, age, species, yield, and climate factors. In the orchards with low soil fertility, high tree age, and high yield, the amount of fertilization is higher; the fertilization of orchards with high soil fertility, low age, and low yield is appropriately reduced. The varieties are more resistant to fertilizers, suitable for climatic conditions, and have a higher amount of water for moderate fertilizers. On the contrary, the amount of fertilizers should be appropriately reduced. If the application amount of organic fertilizer is more, the application amount of chemical fertilizer should be less.
Peach's fertilization period is: base fertilizer, promote flower fertilization, sit fruit fertilizer, fruit enlargement fertilizer.
1. The application of basal fertilizer is based on the difference in different varieties of peach trees. The fertilization time should be applied as soon as possible after the fruit is picked. If the fertilizer cannot be applied in time, it can be applied about one month before the peach defoliation.
2. In the application of basal fertilizers, organic fertilizers are preferred. Under the condition of less organic fertilizer, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer can be determined flexibly according to the age of trees, the growth of peach trees, and the fertility of the soil. The application rate of nitrogen fertilizer in general basal fertilizer accounts for about 40%-60% of the total annual amount of fertilizer. The amount of fertilizer applied per adult peach tree is equivalent to 0.3-0.6 kg of pure nitrogen (equivalent to 1.7-3.4 kg of ammonium bicarbonate or urea 0.6- 1.3 kg or ammonium nitrate 0.9-1.9 kg). General phosphate fertilizer is mainly used as basal fertilizer. If more organic fertilizer is applied at the same time, the pure phosphorus pentoxide equivalent per plant is 0.3-0.5 kg (corresponds to 25% of superphosphate with a phosphorus content of 2-3.3 kg or phosphorus 40% ammonium phosphate 0.75-1.25 kg). The amount of potash used in general basal fertilizers is equivalent to 0.25-0.5 kg of pure potassium oxide (corresponding to 0.5-1 kg of potassium sulfate containing 50% of potassium oxide or 0.4-0.8 kg of potassium chloride containing 60% of potassium oxide). Pay attention not to rely too close to the tree body during fertilization. Fertilizer should be properly mixed with the soil to avoid burning roots. Peach trees with more soil moisture content, soil texture more viscous, older tree age, and weaker tree vigor may use higher amounts of fertilization when applying less organic fertilizer, and vice versa.
3. The application of flower-enhancing fertilizers promotes application of flowering fertilizers before flowering in early spring. Fertilizers are mainly nitrogenous fertilizers, accounting for about 10% of the annual fertilization amount, and are combined with irrigation water after the spring, and the nitrogen fertilizer consumption per 667 m 2 is pure nitrogen. It is calculated as 2-5 kilograms (approximately 4.3-10.9 kilograms of urea or 11-28.6 kilograms of ammonium bicarbonate). If the application rate of basal fertilizer is arrogant or the basal fertilizer applied in winter, the application of flower-fertilizer may not be applied or reduced.
4. The fruit-bearing manure application was mostly applied after flowering and before fruit nucleation, mainly to increase fruit setting rate, improve tree nutrients, and promote rapid fruit growth in the early stage. Nitrogen fertilizer is the main fertilizer, with a small amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. The dosage is about 10% of the annual application amount, and the amount of nitrogen fertilizer per acre is 2-5 kilograms in terms of pure nitrogen (approximately 4.3-10.9 kilograms of urea or 11-28.6 kilograms of ammonium bicarbonate).
5. Application of fruit enlargement fertilizer The fruit enlargement fertilizer is applied after the fruit enters the rapid growth period again. The fruit enlargement period of mid-late maturing varieties basically coincides with the flower bud differentiation period. At this time, top dressing promotes rapid fruit growth and promotes flower bud differentiation, which will be used for the next year's production. A good foundation is of great significance. The fruit enlargement fertilizer is dominated by nitrogen and potassium fertilizers, and a certain amount of phosphate fertilizer can be appropriately applied according to the phosphorus supply status of the soil. The amount of fertilizer used accounts for about 20%-30% of the annual application amount, and the amount of nitrogen fertilizer per 667 m 2 is 4-10 kg in terms of pure nitrogen (approximately 8.6-20.8 kg of urea or 22-57.5 kg of ammonium bicarbonate); potassium fertilizer For every 667m2 application, 6-15kg in terms of potassium oxide (approximately 12-30kg of potassium sulfate containing 50% of potassium oxide or 10-25kg of potassium chloride containing 60% of potassium oxide). . If necessary, 10-30 kg of superphosphate containing 14%-16% of phosphorus pentoxide can be formulated.
6. Peach has less demand for trace element fertilizers, mainly relying on organic fertilizers and soils. If organic fertilizers are used more, they may not be applied or applied less; trace organic fertilizers may be applied less if organic fertilizers are used less frequently. The actual amount of trace fertilizer is calculated as base fertilizer for specific fertilizers: borax 667 m2 dosage 0.25-0.5 kg, zinc sulfate 667 m2 dosage 2-4 kg, manganese sulfate 667 m2 dosage 1-2 kg, ferrous sulfate 667 m2 dosage 5-10 kg (should be used together with high-quality organic fertilizer, the ratio of the ratio of organic fertilizer and iron fertilizer 5:1), micro-fertilizer can also be foliar spray, the concentration of spraying according to the degree of aging leaves The control is 0.1%-0.5%. It should be thin when the leaves are tender and thick when the leaves are older.
Kangerjian round type LED Operating Light LED bulb from OSRAM ,do not engender infrared ray and ultraviolet radiation, it doesn`t have the temperature rise and tissue damage caused by halogen shadowless light, can accelerate the wound healing after surgery, and has no Radiation pollution
Variety of Surgical environment lighting mode: bright, normal, endoscopic lighting mode.
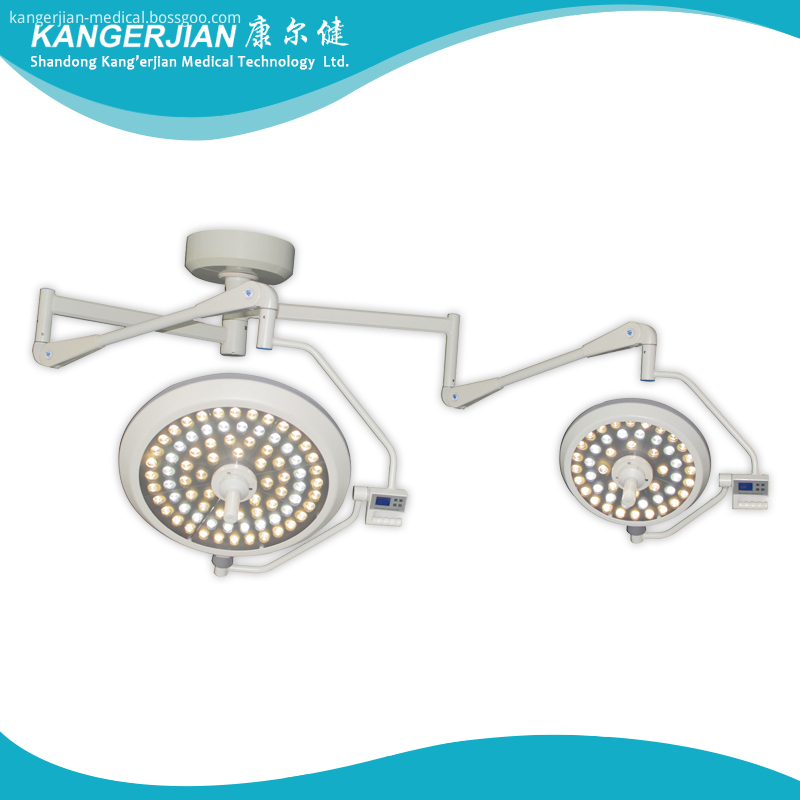
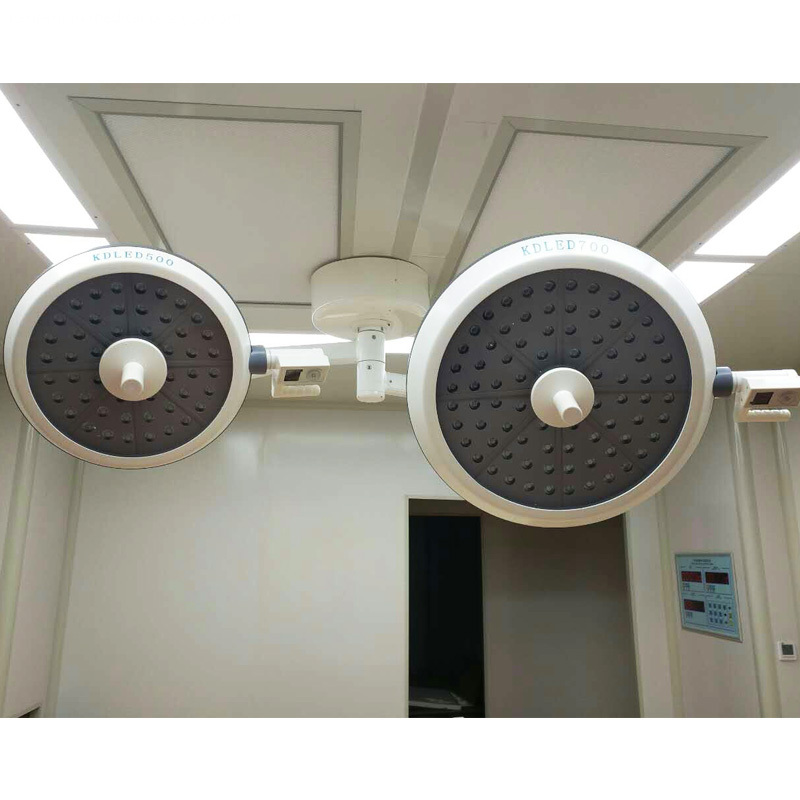


Round Type Operating Light,LED Surgery Light,Led Surgery Ceiling Lamp,Surgical Shadowless Lamp
Shandong qufu healthyou Medical Technology co.,Ltd , https://www.kangerjian-medical.com